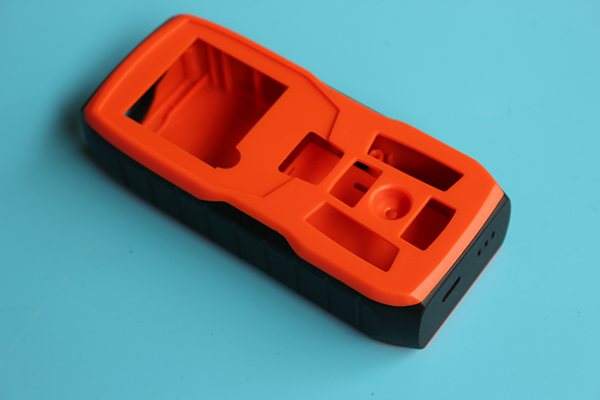
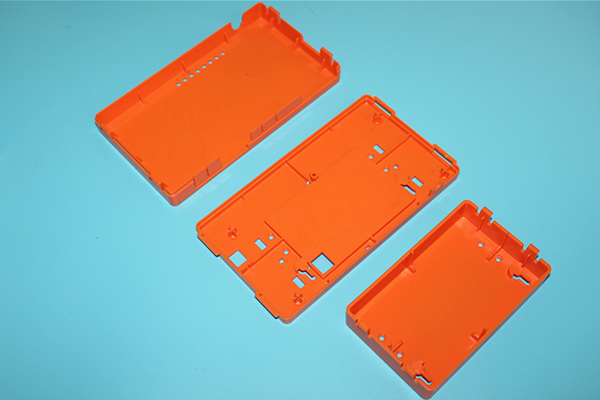


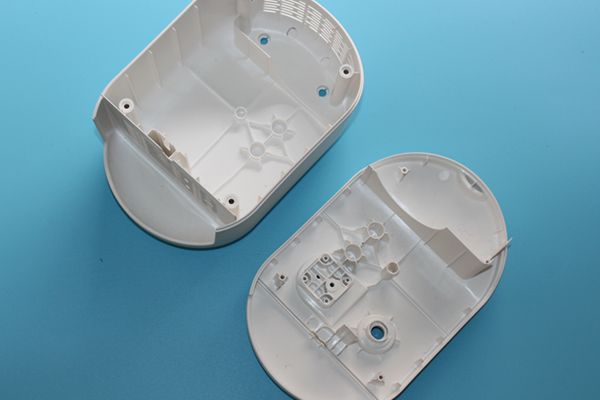
The versatility of Klak-Ling injection molded parts is evident in their widespread use across the electronics industry. These parts are essential components in 3C products – which encompass computers, communication devices, and consumer electronics. They are also integral to the construction of mobile phones and battery casings, among other applications.
Klak-Ling The overall product development process is described as follows
1. Conceptualization and Specification:
- Start by understanding the product requirements, including its dimensions, function, and material specifications. This involves collaborating with product designers to ensure the mold will meet the necessary standards.
2. Material Selection:
- Choose the appropriate material for the mold based on the type of plastic being used, production volume, and desired mold life. Common materials include metal alloys like steel and aluminum.
3. Design and Analysis:
- Use specialized software to create a detailed 3D model of the mold. This includes designing the mold's core, cavity, runner systems, and gates.
- Conduct flow analysis to predict how the molten plastic will fill the mold, ensuring even distribution and avoiding defects.
4. Prototype Development:
- Create a prototype mold, often using additive manufacturing (3D printing) or machining, to test the mold design's feasibility and the final product's functionality.
5. Tool Path Programming:
- Develop precise machine tool paths for CNC machining to manufacture the mold parts. This step includes defining the sequence of operations, cutting tools, and machining parameters.
6. Machining and Fabrication:
- Execute the machining processes using CNC machines to shape the mold components. This step involves drilling, milling, EDM, and grinding to achieve the desired precision and surface finish.
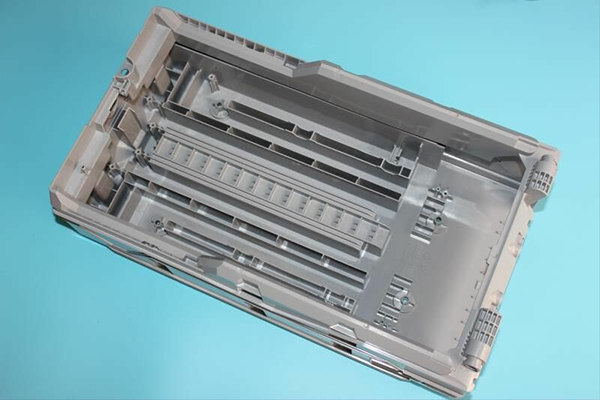
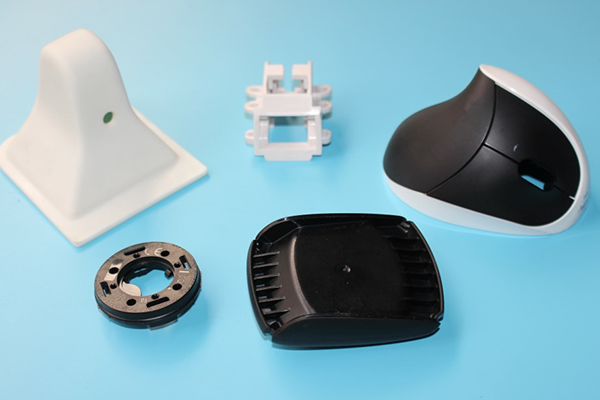


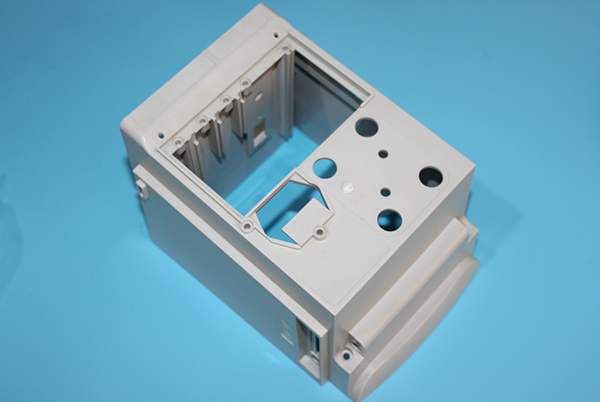
7. Assembly and Testing:
- Assemble the mold components and test the mold to ensure it functions correctly. This includes checking for proper alignment, seal integrity, and ejection mechanism efficiency.
8. Final Adjustments and Refinement:
- Make any necessary adjustments to address issues found during testing. This could involve modifying the mold design, adjusting tolerances, or improving surface finishes.
9. Production Testing:
- Run a trial production to ensure the mold consistently produces parts that meet quality standards. This step is crucial for identifying any issues that might arise during mass production.
10. Documentation and Finalization:
- Document the entire process for future reference, including the design specifications, testing results, and any modifications made during development. Finalize the mold for production, ensuring all details are correct and ready for manufacturing.
Each of these steps requires collaboration across various disciplines, including engineering, material science, and manufacturing. The goal of the plastic mold design process is to develop a reliable, efficient, and high-quality mold that meets the specific needs of the plastic product being produced.



Post time: Oct-29-2024
